What is it?
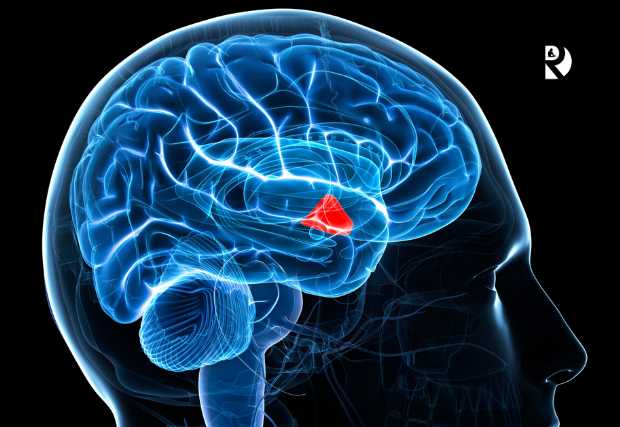
The hypothalamus, a small but crucial part of the brain, plays a significant role in maintaining the body’s internal balance, or homeostasis. Located at the base of the brain, it acts as a control center for various autonomic processes, regulating functions such as temperature, hunger, thirst, sleep, and hormonal activity.
By orchestrating these functions, the hypothalamus ensures that our bodies operate smoothly and adapt to changing conditions. Understanding its role can provide valuable insights into how disruptions in its function can lead to health issues, including depression.
Signs of Dysfunction
When the hypothalamus does not function correctly, it can manifest through various signs and symptoms, including:
- Mood Changes: Persistent sadness, anxiety, or irritability.
- Sleep Disturbances: Insomnia, difficulty staying asleep, or excessive sleepiness.
- Appetite and Weight Fluctuations: Unexplained weight gain or loss, changes in appetite.
- Temperature Regulation Issues: Feeling unusually hot or cold, excessive sweating.
- Fatigue: Chronic tiredness and lack of energy.
- Hormonal Imbalances: Irregular menstrual cycles, reduced libido, or other endocrine-related symptoms.
Causes
Several factors can contribute to hypothalamic dysfunction and exacerbate symptoms of depression:
- Chronic Stress: Prolonged exposure to stress can alter hypothalamic function.
- Genetic Predisposition: A family history of depression or hypothalamic disorders can increase risk.
- Medical Conditions: Tumors, infections, or traumatic brain injuries affecting the hypothalamus.
- Neurotransmitter Imbalance: Disruption in the levels of serotonin, dopamine, or other neurotransmitters.
- Nutritional Deficiencies: Inadequate intake of essential nutrients can impair hypothalamic function.
Diagnosis
Diagnosing hypothalamic dysfunction involves a comprehensive approach:
- Medical History: Detailed discussion of symptoms, duration, and family history.
- Physical Examination: Assessment of neurological and physical signs.
- Laboratory Tests: Blood tests to evaluate hormone levels and rule out other conditions.
- Imaging Studies: MRI or CT scans to detect structural abnormalities in the hypothalamus.
Treatment Options
Effective treatment for hypothalamic dysfunction and associated depression includes:
- Medications: Antidepressants to correct neurotransmitter imbalances; hormone replacement therapy for endocrine issues.
- Therapy: Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) and other forms of psychotherapy to address emotional and behavioral symptoms.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Regular exercise, balanced diet, and adequate sleep to support overall health.
- Stress Management: Techniques such as mindfulness, meditation, and relaxation exercises to reduce stress levels.
Prevention
Preventing hypothalamic dysfunction involves maintaining a healthy lifestyle and managing stress:
- Stress Reduction: Practice stress management techniques, such as yoga, meditation, and deep-breathing exercises.
- Healthy Diet: Ensure a balanced intake of essential nutrients, including omega-3 fatty acids, vitamins, and minerals.
- Regular Exercise: Engage in regular physical activity to support overall health.
- Adequate Sleep: Maintain a consistent sleep schedule and create a restful sleeping environment.
- Regular Medical Check-ups: Monitor your health with routine check-ups and discuss any concerns with your healthcare provider.
Talking to Your Doctor
When discussing symptoms of depression or hypothalamic dysfunction with your doctor:
- Be Honest: Share detailed information about your symptoms, duration, and any changes you’ve noticed.
- Ask Questions: Inquire about potential causes, diagnostic tests, and treatment options.
- Discuss Treatment Plans: Work with your doctor to develop a personalized treatment plan that addresses your specific needs.
Disclaimer
This article is for educational purposes based on research and should not substitute professional medical advice. Always consult your primary care doctor or a qualified healthcare provider regarding your specific health concerns.